# LeetCode 2
2021.3
- 303. Range Sum Query - Immutable(区域和检索 - 数组不可变)
- 304. Range Sum Query 2D - Immutable(二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变)
- 338. 比特位计数
- 354. Russian Doll Envelopes(俄罗斯套娃信封问题)
- 739. 每日温度
- 503. Next Greater Element II(下一个更大元素 II)
- 232. Implement Queue using Stacks(用栈实现队列)
- 125. Valid Palindrome(验证回文串)
- 189. 旋转数组
- 122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II(买卖股票的最佳时机 II)
- 217. Contains Duplicate(存在重复元素)
- 136. Single Number(只出现一次的数字)
- 350. Intersection of Two Arrays II(两个数组的交集 II)
- 66. 加一
- 283. Move Zeroes(移动零)
- 70. Climbing Stairs(爬楼梯)
- 28. Implement strStr() (实现 strStr())
- 38. Count and Say(外观数列)
- 344. Reverse String(反转字符串)
- 387. First Unique Character in a String(字符串中的第一个唯一字符)
- 14. Longest Common Prefix(最长公共前缀)
- 1047. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String(删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项)
- 206. Reverse Linked List(反转链表)
- 234. Palindrome Linked List(回文链表)
- 237. 删除链表中的节点
- 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists(合并两个有序链表)
- 141. Linked List Cycle(环形链表)
- 88. 合并两个有序数组
- 278. First Bad Version(第一个错误的版本)
- 98. Validate Binary Search Tree
- 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
- 101. 对称二叉树
- 102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
- 191. 位1的个数
- 108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree(将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树)
- 169. Majority Element
- 331. Verify Preorder Serialization of a Binary Tree
- 190. Reverse Bits
- 268. 丢失的数字
- 20. Valid Parentheses
- 118. 杨辉三角
- 461. Hamming Distance(汉明距离)
- 412. Fizz Buzz
- 326. 3的幂
- 204. Count Primes(计数质数)
- 705. Design HashSet(设计哈希集合)
- 53. Maximum Subarray(最大子序和)
- 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
- 198. 打家劫舍
- 384. 打乱数组
- 155. Min Stack(最小栈)
- 706. Design HashMap(设计哈希映射)
- 54. Spiral Matrix(螺旋矩阵)
- 94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal(二叉树的中序遍历)
- 59. Spiral Matrix II(螺旋矩阵 II)
- 103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal(二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历)
- 2. Add Two Numbers(两数相加)
- 328. Odd Even Linked List(奇偶链表)
- 115. Distinct Subsequences(不同的子序列)
- 116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node(填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针)
- 230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
- 200. Number of Islands(岛屿数量)
- 160. 相交链表
- 92. Reverse Linked List II(反转链表 II)
- 22. Generate Parentheses(括号生成)
- 46. Permutations(全排列)
- 78. Subsets(子集)
- 79. Word Search(单词搜索)
- 1603. Design Parking System(设计停车系统)
- 55. 跳跃游戏
- 62. 不同路径
- 150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation(逆波兰表达式求值)
- 322. 零钱兑换
- 300. 最长递增子序列
- 73. Set Matrix Zeroes(矩阵置零)
- 297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
- 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1)(常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素)
- 202. 快乐数
- 172. Factorial Trailing Zeroes(阶乘后的零)
- 171. Excel表列序号
- 50. Pow(x, n)
- 3. 无重复字符的最长子串
- 5. 最长回文子串
- 334. Increasing Triplet Subsequence(递增的三元子序列)
- 456. 132 模式
- 82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II(删除排序链表中的重复元素 II)
- 371. 两整数之和
- 83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
- 69. Sqrt(x)(x 的平方根)
- 61. Rotate List(旋转链表)
- 173. Binary Search Tree Iterator(二叉搜索树迭代器)
- 347. Top K Frequent Elements(前 K 个高频元素)
- 215. Kth Largest Element in an Array(数组中的第K个最大元素)
- 162. 寻找峰值
- 240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
- 29. 两数相除
- 166. Fraction to Recurring Decimal(分数到小数)
- 621. Task Scheduler(任务调度器)
- 105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal(从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树)
- 74. Search a 2D Matrix
- 90. Subsets II(子集 II)
# 303. Range Sum Query - Immutable(区域和检索 - 数组不可变)
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class RangeSumQuery {
@Parameters
public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{new int[]{-2, 0, 3, -5, 2, -1}, 0, 2, 1},
{new int[]{-2, 0, 3, -5, 2, -1}, 2, 5, -1},
{new int[]{-2, 0, 3, -5, 2, -1}, 0, 5, -3},
{new int[]{}, 0, 5, 0},
});
}
@Parameter
public int[] nums;
@Parameter(1)
public int i;
@Parameter(2)
public int j;
@Parameter(3)
public int expect;
@Test
public void test() {
NumArray na = new NumArray(nums);
int result = na.sumRange(i, j);
Assert.assertEquals(expect, result);
}
// 解题方法1.前缀合 2.分块
class NumArray {
int[] nums;
int[] sum;
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
int n = nums.length;
if (n < 1) {
sum = new int[0];
return;
}
sum = new int[n + 1];
sum[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + nums[i];
}
}
public int sumRange(int i, int j) {
if (i >= nums.length || j > nums.length) {
return 0;
}
return sum[j] - sum[i] + nums[i];
}
}
}
# 304. Range Sum Query 2D - Immutable(二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变)
递归,回溯,超时:
class NumMatrix {
int[][] sum;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int row = matrix.length;
if (row == 0) {
sum = new int[0][0];
return;
}
int col = matrix[0].length;
sum = new int[row + 1][col + 1];
recursive(matrix, row, col);
}
public int recursive(int[][] matrix, int row, int col) {
if (row - 1 < 0 || col - 1 < 0) {
return 0;
}
sum[row][col] = matrix[row - 1][col - 1]
+ recursive(matrix, row - 1, col)
+ recursive(matrix, row, col - 1)
- recursive(matrix, row - 1, col - 1);
return sum[row][col];
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
if (sum.length == 0 || sum[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return sum[row2 + 1][col2 + 1] + sum[row1][col1] - sum[row1][col2 + 1] - sum[row2 + 1][col1];
}
}
二维前缀和,思路参考下图:
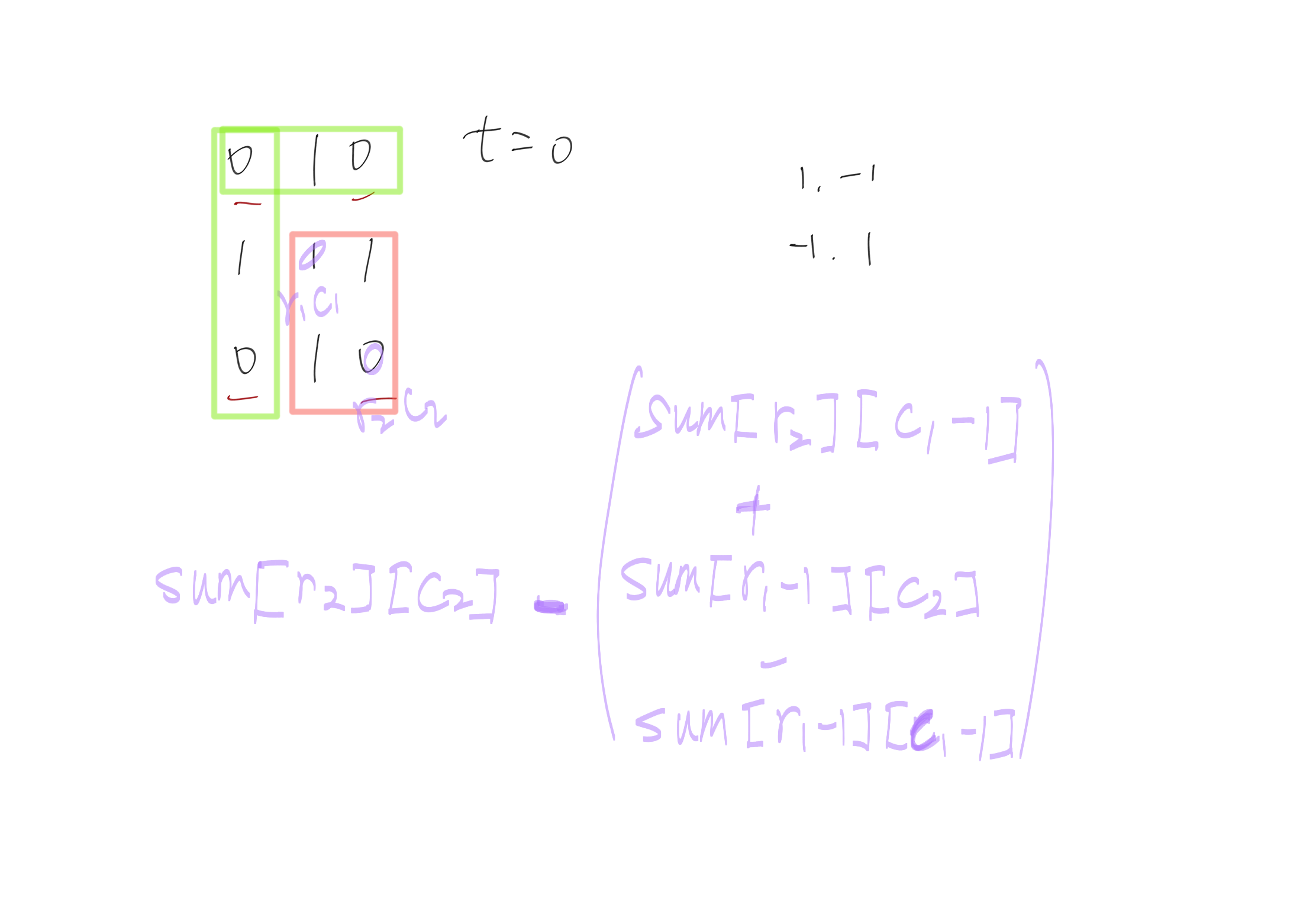
class NumMatrix {
int[][] presum;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int[][] ma = matrix;
int n = matrix.length;
int m = matrix[0].length;
presum = new int[n+1][m+1];
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
presum[r+1][c+1] = presum[r+1][c] + presum[r][c+1] - presum[r][c] + ma[r][c];
}
}
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
return presum[row2+1][col2+1] - presum[row2+1][col1] - presum[row1][col2+1] + presum[row1][col1];
}
}
# 338. 比特位计数
同:剑指 Offer II 003. 前 n 个数字二进制中 1 的个数
// [0 1 1 2 1 2]
// n&(n-1) 代表,如果偶数,能获得n-2的值,如果是奇数,获得n-1的值,如果是2的精确幂,则是0。
// n&(n-1) 会找出n是0还是2的精确幂。
public int[] countBits(int num) {
int[] res = new int[num+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
res[i] = res[i & (i - 1)] + 1;
}
return res;
}
动态规划,右移一位,获取之前计算的结果,然后加上右移移除的那一位数(可能0或1):
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] res = new int[n+1];
int i = 0;
while (i++ < n) {
res[i] = res[i>>>1] + (i&1);
}
return res;
}
}
与第一个解相同,一个月后再次写,这个解的规律不容易发现:
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] res = new int[n+1];
int i = 0;
while (i++ < n) {
res[i] = res[i&(i-1)] + 1;
}
return res;
}
}
一年后再写,虽然发现了规律,但是没有想到用位运算来解决。
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] res = new int[n+1];
res[0] = 0;
int next = 1;
int i = 1;
int add = 0;
while (i <= n) {
if (i == next) {
add = 0;
next = next * 2;
}
res[i] = 1 + res[add];
add++
i++;
}
return res;
}
}
# 354. Russian Doll Envelopes(俄罗斯套娃信封问题)
// 宫水三叶 题解
class Solution {
public int maxEnvelopes(int[][] es) {
int n = es.length;
if (n == 0) return n;
// 由于我们使用了 g 记录高度,因此这里只需将 w 从小到达排序即可
Arrays.sort(es, (a, b)->a[0] - b[0]);
// f(i) 为考虑前 i 个物品,并以第 i 个物品为结尾的最大值
int[] f = new int[n];
// g(i) 记录的是长度为 i 的最长上升子序列的最小「信封高度」
int[] g = new int[n];
// 因为要取 min,用一个足够大(不可能)的高度初始化
Arrays.fill(g, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
g[0] = 0;
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 0, j = 0, len = 1; i < n; i++) {
// 对于 w 相同的数据,不更新 g 数组,从而保证 g 中只会出现满足 w 严格小于当前信封的「历史信封」
if (es[i][0] != es[j][0]) {
// 限制 j 不能越过 i,确保 g 数组中只会出现第 i 个信封前的「历史信封」
while (j < i) {
int prev = f[j], cur = es[j][1];
if (prev == len) {
// 与当前长度一致了,说明上升序列多增加一位
g[len++] = cur;
} else {
// 始终保留最小的「信封高度」,这样可以确保有更多的信封可以与其行程上升序列
// 举例:同样是上升长度为 5 的序列,保留最小高度为 5 记录(而不是保留任意的,比如 10),这样之后高度为 7 8 9 的信封都能形成序列;
g[prev] = Math.min(g[prev], cur);
}
j++;
}
}
// 二分过程
// g[i] 代表的是上升子序列长度为 i 的「最小信封高度」
int l = 0, r = len;
while (l < r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
// 令 check 条件为 es[i][1] <= g[mid](代表 w 和 h 都严格小于当前信封)
// 这样我们找到的就是满足条件,最靠近数组中心点的数据(也就是满足 check 条件的最大下标)
// 对应回 g[] 数组的含义,其实就是找到 w 和 h 都满足条件的最大上升长度
if (es[i][1] <= g[mid]) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
// 更新 f[i] 与答案
f[i] = r;
ans = Math.max(ans, f[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}
# 739. 每日温度
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class DailyTemperatures {
@Parameters
public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{new int[]{73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73}, new int[]{1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0}},
{new int[]{73}, new int[]{0}},
});
}
@Parameter
public int[] nums;
@Parameter(1)
public int[] expect;
@Test
public void test() {
int[] result = dailyTemperatures(nums);
Assert.assertArrayEquals(expect, result);
}
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] nums) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int n = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i] > nums[stack.peek()]) {
int pop = stack.pop();
res[pop] = i - pop;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return res;
}
// 数组替代单调栈的方法,数组更快,内存消耗更低。
public int[] dailyTemperatures2(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] stack = new int[n];
int pop = -1;
int[] res = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (pop >= 0 && nums[i] > nums[stack[pop]]) {
int min = stack[pop--];
res[min] = i - min;
}
stack[++pop] = i;
}
return res;
}
}
重刷,使用单调栈,写法上还是复杂了
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
// int[]{index, value}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int[] res = new int[temperatures.length];
for (int i = 0; i < temperatures.length; i++) {
if (stack.empty() || temperatures[i] <= temperatures[stack.peek()]) {
stack.push(i);
} else {
while (!stack.empty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {
int pop = stack.pop();
res[pop] = i-pop;
}
stack.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
}
# 503. Next Greater Element II(下一个更大元素 II)
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class NextGreaterElementII {
@Parameters
public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{new int[]{1, 2, 1}, new int[]{2, -1, 2}},
{new int[]{0}, new int[]{-1}},
});
}
@Parameter
public int[] nums;
@Parameter(1)
public int[] expect;
@Test
public void test() {
int[] result = nextGreaterElements(nums);
Assert.assertArrayEquals(expect, result);
}
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] stack = new int[n];
int pop = -1;
int[] res = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(res, -1);
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n * 2; i++, j = i % n) {
while (pop >= 0 && nums[j] > nums[stack[pop]]) {
int min = stack[pop--];
res[min] = nums[j];
}
if (res[j] <= 0 && pop + 1 < n) {
stack[++pop] = j;
}
}
return res;
}
}
# 232. Implement Queue using Stacks(用栈实现队列)
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class ImplementQueueUsingStacks {
@Parameters
public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{1,2},
});
}
@Parameter
public int a;
@Parameter(1)
public int b;
@Test
public void test() {
MyQueue q = new MyQueue();
q.push(a);
Assert.assertEquals(a, q.peek());
q.push(b);
Assert.assertEquals(a, q.peek());
Assert.assertEquals(a, q.pop());
Assert.assertEquals(b, q.pop());
Assert.assertTrue(q.empty());
}
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> in = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> out = new Stack<>();
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
in.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
dao();
return out.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
dao();
return out.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return out.empty()&&in.empty();
}
public void dao(){
if(out.isEmpty()){
while (!in.isEmpty()) {
out.push(in.pop());
}
}
}
}
}
# 125. Valid Palindrome(验证回文串)
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class ValidPalindrome {
@Parameters
public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama", true},
});
}
@Parameter
public String s;
@Parameter(1)
public boolean expect;
@Test
public void test() {
boolean result = isPalindrome(s);
Assert.assertEquals(expect, result);
}
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
// 只保留字母和数字
s = keepNumberAndAlphabet(s);
// 翻转过来
String r = reverse(s);
// 与原字符串比较
return r.equalsIgnoreCase(s);
}
private String reverse(String s) {
return new StringBuffer(s).reverse().toString();
}
private String keepNumberAndAlphabet(String s) {
return s.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]", "");
}
}
# 189. 旋转数组
暴力法,On空间复杂度:
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res[i] = nums[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nums[(i+k)%n] = res[i];
}
}
}
环状替换,没太看懂 - -:
// TODO
多次翻转链表,O1的空间复杂度:
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
k = k % n;
reverse(nums, 0, n-1);
reverse(nums, 0, k-1);
reverse(nums, k, n-1);
}
private void reverse(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
int tmp = nums[start];
nums[start] = nums[end];
nums[end] = tmp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
}
# 122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II(买卖股票的最佳时机 II)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] p) {
int n = p.length;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
res += Math.max(0, p[i] - p[i-1]);
}
return res;
}
}
一个月后再来做,提交的代码如下,代码存在重复逻辑,不清晰,可以简化成上面的标准答案。
// 本题求上升数字中的差值,累加差值即可。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] p) {
int n = p.length;
int max = 0;
int pre = p[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (p[i] <= pre) {
pre = p[i];
} else if (p[i] > pre) {
max += p[i]-pre;
pre = p[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
简化后,基本和第一版题解一致了: 本来就只是用前一个值,直接下标减一即可,为啥还要单独用变量存起来,傻子阿
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] p) {
int max = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < p.length; i++) {
if (p[i] > p[i-1]) {
max += p[i] - p[i-1];
}
}
return max;
}
}
# 217. Contains Duplicate(存在重复元素)
// 1.set judge duplicate
class Solution {
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i< n; i++) {
if (set.contains(nums[i])) {
return true;
} else {
set.add(nums[i]);
}
}
return false;
}
}
# 136. Single Number(只出现一次的数字)
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res ^= nums[i];
}
return res;
}
}
# 350. Intersection of Two Arrays II(两个数组的交集 II)
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class IntersectionOfTwoArraysII {
@Parameters
public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{new int[]{1, 2, 2, 1}, new int[]{2, 2}, new int[]{2, 2}},
});
}
@Parameter
public int[] nums1;
@Parameter(1)
public int[] nums2;
@Parameter(2)
public int[] expect;
@Test
public void test() {
int[] result = intersect(nums1, nums2);
Assert.assertArrayEquals(expect, result);
}
public int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int n = nums1.length;
int m = nums2.length;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Integer tmp = map.get(nums1[i]);
if (tmp == null) {
map.put(nums1[i], 1);
} else {
map.put(nums1[i], tmp + 1);
}
}
int[] res = new int[n];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
Integer tmp = map.get(nums2[i]);
if (tmp != null && tmp != 0) {
res[index++] = nums2[i];
map.put(nums2[i], tmp - 1);
}
}
return Arrays.copyOfRange(res, 0, index);
}
}
# 66. 加一
public int[] plusOne(int[] d) {
int n = d.length;
int up = 1;
for (int i = n-1; i > -1; i--) {
int tmp = d[i] + up;
if (tmp >= 10) {
up = 1;
} else {
up = 0;
}
d[i] = tmp % 10;
}
if (up > 0) {
int[] res = new int[n+1];
res[0] = 1;
System.arraycopy(d, 0, res, 1, n);
return res;
}
return d;
}
func plusOne(digits []int) []int {
n := len(digits)
d := digits[0:n]
plus := 1
for i := n-1; i >= 0; i-- {
d[i] = d[i] + plus
if d[i] > 9 {
plus = 1
d[i] = 0
} else {
plus = 0
break
}
}
if plus == 1 {
d[0] = 0
d = append([]int{1}, d...)
}
return d
}
# 283. Move Zeroes(移动零)
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
swap(nums, i, idx);
idx++;
}
}
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int a, int b) {
int tmp = nums[a];
nums[a] = nums[b];
nums[b] = tmp;
}
}
go解法,朴素思路,利用两个指针,当外层循环遍历到0时,就起一个新的指针+1开始往后内循环,找到第一个不等于0的数,与外循环指针进行交换,随后break内循环,从外循环继续:
func moveZeroes(nums []int) {
n := len(nums)
for i, val := range nums {
if val == 0 {
for j := i+1; j < n; j++ {
if nums[j] != 0 {
swap(nums, i, j)
break
}
}
}
}
}
func swap(nums []int, a, b int) {
nums[a], nums[b] = nums[b], nums[a]
}
两遍循环,利用双指针,第一个指针指向0的位置,第二个指针一致向后移动,如果遇见不等于0的数组,将非0的数交换到0上:
func moveZeroes(nums []int) {
j := 0
for i, val := range nums {
if val != 0 {
nums[j] = nums[i]
j++
}
}
for j < len(nums) {
nums[j] = 0
j++
}
}
也可以遍历数组, 遇到0时,将0删掉,追加到数组最后:
func moveZeroes(nums []int) {
n := len(nums)
zcnt := 1
for i := 0; i < n-zcnt; i++ {
if nums[i] == 0 {
nums = append(nums[:i], nums[i+1:]...)
nums = append(nums, 0)
i--
zcnt++
}
}
}
# 70. Climbing Stairs(爬楼梯)
// f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2)
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<3) return n;
int a = 1, b = 2;
int c = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return c;
}
}
# 28. Implement strStr() (实现 strStr())
class Solution {
// 最快解上优化代码结构 @jesse
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if (needle.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (!haystack.contains(needle)) {
return -1;
}
int i, count = 0;
for (int v = 0; v < haystack.length(); v++) {
i = v;
int j = 0;
for (; j < needle.length(); j++) {
if (needle.charAt(j) == haystack.charAt(i)) {
count++;
i++;
} else {
count = 0;
break;
}
}
if (j == needle.length()) {
if (count == needle.length()) {
return v;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
// 最快解
public int strStr4(String haystack, String needle) {
if (needle.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (!haystack.contains(needle)) {
return -1;
}
int i = 0, count = 0;
for (int v = 0; v < haystack.length(); v++) {
for (int j = v; j < haystack.length(); j++) {
if (needle.charAt(i) == haystack.charAt(j)) {
count++;
i++;
} else {
count = 0;
i = 0;
break;
}
if (count == needle.length()) {
return (j-(needle.length()-1));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
// 最优雅
public int strStr3(String haystack, String needle) {
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
for (int j = 0; ; j++) {
if (j == needle.length()) return i;
if (i + j == haystack.length()) return -1;
if (needle.charAt(j) != haystack.charAt(i + j)) break;
}
}
}
// violent @jesse
// 很慢,for循环上使用了&&条件相比其他解会慢太多
public int strStr2(String a, String b) {
// b in a
char[] ac = a.toCharArray();
char[] bc = b.toCharArray();
int al = ac.length;
int bl = bc.length;
if (bl == 0) {
return bl;
}
if (bl > al) {
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < al; i++) {
boolean match = true;
int j = 0, itemp = i;
for (; j < bl && itemp < al; j++, itemp++) {
if (ac[itemp] != bc[j]) {
match = false;
break;
}
}
if (j != bl) {
match = false;
}
if (match) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
一个月后再刷:
class Solution {
public int strStr(String h, String n) {
// n is null or ""
if (n == null || "".equals(n)) {
return 0;
}
// 滑动窗口
int len = h.length();
int l = 0, r = n.length();
while (r <= len) {
if (h.substring(l, r).equals(n)) {
return l;
}
l++;
r++;
}
return -1;
}
}
# 38. Count and Say(外观数列)
class Solution {
// for循环解决
public String countAndSay(int n) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("1");
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
sb = recursive(sb);
}
return sb.toString();
}
private StringBuilder recursive(StringBuilder sb) {
StringBuilder nsb = new StringBuilder();
char pre = sb.charAt(0);
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < sb.length(); i++) {
if (sb.charAt(i) == pre) {
cnt++;
} else {
// current -> pre
// concat string
nsb.append(cnt);
nsb.append(pre);
pre = sb.charAt(i);
cnt = 1;
}
}
nsb.append(cnt);
nsb.append(pre);
return nsb;
}
}
# 344. Reverse String(反转字符串)
class Solution {
public void reverseString(char[] s) {
int n = s.length;
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while (l < r) {
swap(s, l, r);
l++;
r--;
}
}
private void swap(char[] s, int l, int r) {
char t = s[l];
s[l] = s[r];
s[r] = t;
}
}
# 387. First Unique Character in a String(字符串中的第一个唯一字符)
class Solution {
public int firstUniqChar(String s) {
int[] set = new int[26];
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
int n = c.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
set[c[i] - 'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (set[c[i] - 'a'] == 1) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
# 14. Longest Common Prefix(最长公共前缀)
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] s) {
int n = s.length;
if (n == 0) {
return "";
}
String comm = s[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
comm = longestCommonPrefix(comm, s[i]);
}
return comm;
}
private String longestCommonPrefix(String a, String b) {
int n = Math.min(a.length(), b.length());
String comm = "";
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a.charAt(i) != b.charAt(i)) {
break;
}
index++;
}
if (index > -1) {
comm = a.substring(0, index + 1);
}
return comm;
}
}
# 1047. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String(删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项)
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicates(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (!stack.empty() && stack.peek().equals(s.charAt(i))) {
stack.pop();
} else {
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
}
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (!stack.empty()) {
sb.append(stack.pop());
}
return sb.reverse().toString();
}
}
# 206. Reverse Linked List(反转链表)
class Solution {
// @jesse
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 1->2->3
ListNode tail = null;
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
while (head.next != null) {
ListNode tmp = head;
head = head.next;
tmp.next = tail;
tail = tmp;
}
head.next = tail;
return head;
}
}
时隔4个月后再做,写法更简洁了:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur!=null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
# 234. Palindrome Linked List(回文链表)
class Solution {
// [1,1,2,1]
// [1,2,2,1]
// [1,2,3,2,1]
// [2,2,2]
// [2,2,2,2]
// [3,2,3,1]
// [1]
// [1,2]
// [2,2]
public boolean isPalindrome2(ListNode head) {
// reverse half list, two points(fast&slow)
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 奇偶数节点处理
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode tail = reverse(slow);
while (tail != null) {
if (head.val != tail.val) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
tail = tail.next;
}
return true;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode tail = null;
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
while (head.next != null) {
ListNode tmp = head;
head = head.next;
tmp.next = tail;
tail = tmp;
}
head.next = tail;
return head;
}
public ListNode front;
// @题解 递归
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// 利用递归
front = head;
return recursive(head);
}
private boolean recursive(ListNode node) {
// recursive term condition
if (node == null) {
return true;
}
// compare
boolean res = (recursive(node.next) && front.val == node.val);
// two point go next
front = front.next;
return res;
}
}
# 237. 删除链表中的节点
//sb?
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
# 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists(合并两个有序链表)
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode node = head;
while (a != null && b != null) {
if (a.val <= b.val) {
node.next = a;
a = a.next;
} else {
node.next = b;
b = b.next;
}
node = node.next;
}
while (a != null) {
node.next = a;
a = a.next;
node = node.next;
}
while (b != null) {
node.next = b;
b = b.next;
node = node.next;
}
return head.next;
}
}
func mergeTwoLists(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
head := new(ListNode)
var res *ListNode = head
for l1 != nil && l2 != nil {
if l1.Val < l2.Val {
res.Next = l1
l1 = l1.Next
res = res.Next
} else {
res.Next = l2
l2 = l2.Next
res = res.Next
}
}
var l3 *ListNode
if l1 != nil {
l3 = l1
}
if l2 != nil {
l3 = l2
}
for l3 != nil {
res.Next = l3
l3 = l3.Next
res = res.Next
}
return head.Next
}
# 141. Linked List Cycle(环形链表)
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
# 88. 合并两个有序数组
// nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
// nums1 = [1,2,0,0,0], m = 2, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
// nums1 = [1,2,3,4,0,0,0], m = 4, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
// nums1 = [1,3,7,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
// nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] n1, int m, int[] n2, int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return;
}
int a = 0;
while (a < m) {
if (n1[a] <= n2[0]) {
a++;
} else {
swap(n1, a, n2, 0);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
swap2(n1, m + i, n2, i);
}
}
private void swap(int[] n1, int a, int[] n2, int b) {
int tmp = n1[a];
n1[a] = n2[b];
n2[b] = tmp;
for (int i = 1; i < n2.length; i++) {
if (n2[i - 1] > n2[i]) {
swap(n2, i - 1, i);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
private void swap2(int[] n1, int a, int[] n2, int b) {
int tmp = n1[a];
n1[a] = n2[b];
n2[b] = tmp;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int a, int b) {
int tmp = nums[a];
nums[a] = nums[b];
nums[b] = tmp;
}
}
go解法:
func merge(nums1 []int, m int, nums2 []int, n int) {
n1, n2 := nums1, nums2
if n <= 0 {
return
}
i := 0
for j := 0; i < m; {
if n1[i] <= n2[j] {
i++
} else {
n1[i], n2[j] = n2[j], n1[i]
for k := j+1; k < n; k++ {
if n2[k] < n2[k-1] {
n2[k], n2[k-1] = n2[k-1], n2[k]
} else {
break
}
}
}
}
for j := 0 ; i < m+n; i++ {
n1[i], n2[j] = n2[j], n1[i]
j++
}
}
# 278. First Bad Version(第一个错误的版本)
常规做法是通过二分法找到第一个错误的版本,另一种是找到最后一个正确的版本,那错误版本就是再+1即可。
public class Solution extends VersionControl {
// 二分查找
public int firstBadVersion(int n) {
int left = 1, mid = 0, right = n;
while (left < right) {
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (isBadVersion(mid)) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
}
二分法,go:
func firstBadVersion(n int) int {
l, r := 1, n
for l < r {
mid := l + ((r-l)>>1)
if isBadVersion(mid) {
r = mid
} else {
l = mid + 1
}
}
return r
}
找到最后一个正确的版本:
func firstBadVersion(n int) int {
// left从0开始,为了兼容n=1的场景,否则无法进入while循环
l, r := 0, n
for l < r {
mid := l + ((r-l+1)>>1)
if isBadVersion(mid) {
r = mid-1
} else {
l = mid
}
}
return l+1
}
当使用while (l <= r)时:
func firstBadVersion(n int) int {
l, r := 1, n
for l <= r {
mid := l + ((r-l)>>1)
if isBadVersion(mid) {
r = mid-1
} else {
l = mid+1
}
}
return r+1
}
当使用while (l <= r),且mid落点偏右(偏右是寻找最后一个正确版本)时:
func firstBadVersion(n int) int {
l, r := 0, n
for l <= r {
mid := l + ((r-l+1)>>1)
if isBadVersion(mid) {
r = mid-1
} else {
l = mid+1
}
}
return l
}
# 98. Validate Binary Search Tree
class Solution {
// 栈 题解
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if(pre != null && root.val <= pre.val) return false;
pre = root;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
}
// 递归 题解
public boolean isValidBST2(TreeNode root) {
return recursive(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
private boolean recursive(TreeNode node, long left, long right) {
if (node == null) {
return true;
}
if (node.val <= left || node.val >= right) {
return false;
}
return recursive(node.left, left, node.val) && recursive(node.right, node.val, right);
}
}
# 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
class Solution {
int max = 0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
recursive(root, 0);
return max;
}
// d: pre depth
private void recursive(TreeNode n, int d) {
if (n == null) {
max = Math.max(max, d);
return;
}
recursive(n.left, d+1);
recursive(n.right, d+1);
}
}
# 101. 对称二叉树
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return recursive(root, root);
}
private boolean recursive(TreeNode a, TreeNode b) {
if (a == null && b == null) {
return true;
}
if (a != null && b != null) {
if (a.val == b.val && recursive(a.left, b.right) && recursive(a.right, b.left)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
模拟,go解法:
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
return root == nil || recursive(root.Left, root.Right)
}
func recursive(l, r *TreeNode) bool {
if l == nil && r == nil {
return true
}
if l == nil || r == nil || l.Val != r.Val {
return false
}
return recursive(l.Left, r.Right) && recursive(r.Left, l.Right)
}
# 102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
recursive(root, 0);
return res;
}
private void recursive(TreeNode n, int row) {
if (n == null) {
return;
}
List<Integer> data;
if (res.size() <= row) {
data = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(data);
} else {
data = res.get(row);
}
data.add(n.val);
recursive(n.left, row+1);
recursive(n.right, row+1);
}
}
# 191. 位1的个数
就是求汉明重量:
public class Solution {
// you need to treat n as an unsigned value
public int hammingWeight(int i) {
i = (i & 0x55555555) + ((i >> 1) & 0x55555555);
i = (i & 0x33333333) + ((i >> 2) & 0x33333333);
i = (i & 0x0F0F0F0F) + ((i >> 4) & 0x0F0F0F0F);
i = (i * (0x01010101) >> 24);
return i;
}
}
# 108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree(将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树)
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return recursive(nums, 0, nums.length-1);
}
private TreeNode recursive(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if (l > r) {
return null;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
TreeNode n = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
n.left = recursive(nums, l, mid-1);
n.right = recursive(nums, mid+1, r);
return n;
}
}
# 169. Majority Element
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
if (nums[0] == nums[(nums.length/2)]) {
return nums[0];
} else {
return nums[(nums.length/2)];
}
}
}
# 331. Verify Preorder Serialization of a Binary Tree
class Solution {
private char j = '#';
private char d = ',';
public boolean isValidSerialization(String p) {
// 计数
int cnt = 1;
int n = p.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (cnt == 0) return false; // 表示树结构完整,但数组里面还有节点,因此false
char c = p.charAt(i);
if (d == c) continue;
else if (j == c) cnt--;
else {
while (i+1 < n && d != p.charAt(i+1)) {
i++;
}
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt == 0;
}
}
# 190. Reverse Bits
public class Solution {
// you need treat n as an unsigned value
public int reverseBits2(int n) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
int b = n & 1;
n = n >>> 1;
res = (res << 1) | b; // 用或|和异或^都可以
}
return res;
}
// O(1) java.lang.Integer.reverse()方法jdk8的实现
public int reverseBits(int i) {
i = (i & 0x55555555) << 1 | (i >>> 1) & 0x55555555;
i = (i & 0x33333333) << 2 | (i >>> 2) & 0x33333333;
i = (i & 0x0f0f0f0f) << 4 | (i >>> 4) & 0x0f0f0f0f;
i = (i << 24) | ((i & 0xff00) << 8) |
((i >>> 8) & 0xff00) | (i >>> 24);
return i;
}
}
# 268. 丢失的数字
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res ^= nums[i];
res ^= i+1;
}
return res;
}
}
# 20. Valid Parentheses
class Solution {
Map<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<>();
{
map.put('{', '}');
map.put('[', ']');
map.put('(', ')');
}
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> z = new Stack<>();
int n = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (z.empty()) {
z.push(c);
} else {
Character tmp = map.get(z.peek());
if (tmp != null && tmp == c) {
z.pop();
} else {
z.push(c);
}
}
}
return z.empty();
}
}
# 118. 杨辉三角
class Solution {
// 暴力
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int n) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// row
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// every row
List<Integer> r = new ArrayList<>();
r.add(1);
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
// f(row, col) = f(row-1, col-1) + f(row-1, col)
r.add(res.get(i-1).get(j-1) + res.get(i-1).get(j));
}
r.add(1);
res.add(r);
}
res.get(0).remove(1);
return res;
}
}
重刷,思路简单清晰了很多
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
List<Integer> row = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> pre = null;
if (i > 0) pre = res.get(i-1);
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
if (j == 0) {
row.add(1);
} else if (j == i) {
row.add(1);
} else {
row.add(pre.get(j-1)+pre.get(j));
}
}
res.add(row);
}
return res;
}
}
# 461. Hamming Distance(汉明距离)
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int i = x ^ y;
return hammingWeight(i);
}
// 利用汉明重量求1的个数
public int hammingWeight(int i) {
i = (i & 0x55555555) + ((i >> 1) & 0x55555555);
i = (i & 0x33333333) + ((i >> 2) & 0x33333333);
i = (i & 0x0F0F0F0F) + ((i >> 4) & 0x0F0F0F0F);
i = (i * (0x01010101) >> 24);
return i;
}
}
使用n&(n-1)来快速消除下一个1:
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int diff = x ^ y;
int cnt = 0;
while (diff != 0) {
diff &= diff - 1;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
}
# 412. Fizz Buzz
class Solution {
// 暴力法
public List<String> fizzBuzz(int n) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
if (i % 5 == 0) {
res.add("FizzBuzz");
continue;
}
res.add("Fizz");
} else if (i % 5 == 0) {
res.add("Buzz");
} else {
res.add(String.valueOf(i));
}
}
return res;
}
}
# 326. 3的幂
class Solution {
// Integer.MAX_VALUE = 2^32/2 - 1 = 2147483647
// 3⌊log3MaxInt⌋=3⌊19.56⌋=3^19=1162261467
public boolean isPowerOfThree(int n) {
return n > 0 && 1162261467 % n == 0;
}
}
试除法:
class Solution {
public boolean isPowerOfThree(int n) {
while (n > 1 && n % 3 == 0) {
n /= 3;
}
return n == 1;
}
}
# 204. Count Primes(计数质数)
class Solution {
public int countPrimes(int n) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (isPrime(i)) {
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
public static boolean isPrime(int num) {
if (num <= 3) {
return num > 1;
}
// 不在6的倍数两侧的一定不是质数
if (num % 6 != 1 && num % 6 != 5) {
return false;
}
int sqrt = (int) Math.sqrt(num);
for (int i = 5; i <= sqrt; i += 6) {
if (num % i == 0 || num % (i + 2) == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
# 705. Design HashSet(设计哈希集合)
class MyHashSet {
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
int base = 769;
LinkedList[] data;
private int hash(int k) {
return k % base;
}
public MyHashSet() {
data = new LinkedList[base];
}
public void add(int key) {
LinkedList list = data[hash(key)];
if (list == null) {
list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
data[hash(key)] = list;
}
list.add(key);
}
public void remove(int key) {
LinkedList list = data[hash(key)];
if (list == null) {
return;
}
while (list.indexOf(key) != -1) {
list.remove(list.indexOf(key));
}
}
/** Returns true if this set contains the specified element */
public boolean contains(int key) {
LinkedList list = data[hash(key)];
if (list == null) {
return false;
}
return list.indexOf(key) != -1;
}
}
/**
* Your MyHashSet object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyHashSet obj = new MyHashSet();
* obj.add(key);
* obj.remove(key);
* boolean param_3 = obj.contains(key);
*/
# 53. Maximum Subarray(最大子序和)
class Solution {
// 利用额外变量来存储前一个最大值。最优解。
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int max = nums[0];
int pre = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// pre = Math.max(pre+nums[i], nums[i]);
if (pre > 0) {
pre += nums[i];
} else {
pre = nums[i];
}
max = Math.max(pre, max);
}
return max;
}
// 利用数组本身存储值来递推,会修改原数组
public int maxSubArray3(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int max = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i-1] > 0) {
nums[i] += nums[i-1];
}
// nums[i] = Math.max(nums[i-1]+nums[i], nums[i]);
max = Math.max(nums[i], max);
}
return max;
}
// 朴素递归解法
public int maxSubArray2(int[] nums) {
// f(i) = max{f(i-1)+nums[i], nums[i]}
int n = nums.length;
int max = -999999;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
max = Math.max(recursive(nums, i), max);
}
return max;
}
private int recursive(int[] nums, int i) {
if (i < 0) {
return -999999;
}
return Math.max(recursive(nums, i-1)+nums[i], nums[i]);
}
}
一个月后再做:
// 动归方程:dp[i]表示以nums[i]结尾的数,最大的子数组合。
// if dp[i-1] > 0, dp[i] = dp[i-1]+nums[i]
// if dp[i-1] <= 0, dp[i] = nums[i]
// 由于只依赖前一个最大子数组的合,所以可以进一步压缩空间,只用pre变量保存即可。
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// init
int pre = nums[0];
int max = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int tmp;
if (pre > 0) {
tmp = pre + nums[i];
} else {
tmp = nums[i];
}
max = Math.max(max, tmp);
pre = tmp;
}
return max;
}
}
# 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] p) {
int max = 0;
int minI = 0;
int n = p.length;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// get minI & max
if (p[i] < p[minI]) {
minI = i;
} else {
max = Math.max(max, p[i] - p[minI]);
}
}
return max;
}
}
一个月后再做,变量定义混乱,逻辑冗余,代码需要再精简。
// 本题是求,小值在前,大值在后,两者最大差值。
// 解题方法:动归、单调栈
// diff[]: dp数组代表当天卖出的利润最大是多少,
// 动归方程:diff[i] = MAX{diff[i-1], curr-min} (curr > min)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] p) {
int n = p.length;
int max = 0;
int min = p[0];
// 状态数组为差值集,记录当前值与最小值的差
int[] diff = new int[n];
diff[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (p[i] < min) {
min = p[i];
diff[i] = 0;
} else if (p[i] > min) {
diff[i] = Math.max(diff[i-1], p[i]-min);
max = Math.max(max, diff[i]);
} else {
diff[i] = 0;
}
}
return max;
}
}
状态空间压缩后:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] p) {
int n = p.length;
int max = 0;
int min = p[0];
// 状态压缩,不需使用dp数组,只依赖前一个状态,降低空间复杂度
int diff = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (p[i] < min) {
min = p[i];
diff = 0;
} else if (p[i] > min) {
diff = Math.max(diff, p[i]-min);
max = Math.max(max, diff);
} else {
diff = 0;
}
}
return max;
}
}
暴力解法:会超时
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < n; j++) {
res = Math.max(res, prices[j]-prices[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
}
可以看出,要求出最大的利润,是由一个区间中的最大值-最小值(且最小值下标要小于最大值)获得的。因此可以通过一次遍历的过程,动态的更新最小值,一旦最小值更新,则废弃之前的最大值,重新在右边继续寻找最大值,每次找到一个最大值,则max-min去更新答案。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
int res = 0;
int min = prices[0];
int max = prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (prices[i] < min) {
min = prices[i];
max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else {
if (prices[i] > max) {
max = prices[i];
res = Math.max(res, max-min);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
# 198. 打家劫舍
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
// f(i) = max{f(i-2) + nums[i], f(i-1)}
if (nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (nums.length == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
if (nums.length == 2) {
return Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
}
// f(i-2)
int f2 = nums[0];
// f(i-1)
int f1 = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
// f(i)
int f = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
f = Math.max(f2+nums[i], f1);
f2 = f1;
f1 = f;
}
return f;
}
// 递归 会超时
public int rob2(int[] nums) {
// f(i) = max{f(i-2) + nums[i], f(i-1)}
return f(nums, nums.length - 1);
}
private int f(int[] nums, int i) {
if (i > nums.length-1 || i < 0) {
return 0;
}
if (i == 1) {
return Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
}
if (i == 0) {
return nums[0];
}
return Math.max(f(nums, i-2) + nums[i], f(nums, i-1));
}
}
- 迭代(未压缩空间,使用原始大小dp数组空间)
// 动归方程:dp[i] = max(dp[i-1], dp[i-2]+Vi);
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
// 边界场景
int n = nums.length;
if (n < 1) {
return 0;
} else if (n < 2) {
return nums[0];
} else if (n < 3) {
return Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
}
// 初始化,dp0,dp1,属于迭代初始依赖数据
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
// 迭代,从第三个房间开始,前两个已经初始化了
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1], dp[i-2]+nums[i]);
}
return dp[n-1];
}
}
一个月后再做,直接使用最简动归,秒解:
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
// f(n) = Math.max(f(n-1) , f(n-2) + val)
int p1 = 0, p2 = nums[0];
if (nums.length < 2) {
return p2;
}
p1 = Math.max(p2, nums[1]);
for (int i = 2 ; i < nums.length; i++) {
int max = Math.max(p1, p2+nums[i]);
p2 = p1;
p1 = max;
}
return p1;
}
}
几个月后再做,写法更简洁清晰了
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int i1 = 0, i2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int c = Math.max(i2+nums[i], i1);
i2 = i1;
i1 = c;
}
return i1;
}
}
# 384. 打乱数组
class Solution {
int[] nums;
int[] origin;
Random rand = new Random();
public Solution(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
this.origin = nums.clone();
}
/** Resets the array to its original configuration and return it. */
public int[] reset() {
return origin;
}
/** Returns a random shuffling of the array. */
public int[] shuffle() {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
swap(nums, i, rand.nextInt(n-i)+i);
}
return nums;
}
private void swap(int[] n, int a, int b) {
int t = n[a];
n[a] = n[b];
n[b] = t;
}
}
一样的做法,稍微不同的代码写法而已:
class Solution {
int[] nums;
public Solution(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
}
public int[] reset() {
return nums;
}
public int[] shuffle() {
int[] res = nums.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int j = (int) (Math.random() * (nums.length-i)) + i;
swap(res, i, j);
}
return res;
}
private void swap(int[] ns, int i, int j) {
int tmp = ns[i];
ns[i] = ns[j];
ns[j] = tmp;
}
}
# 155. Min Stack(最小栈)
// todo 待实现,使用差值,不用额外栈。
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<>();
Integer min = null;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
}
public void push(int x) {
if (min == null) {
min = x;
}
x =
s.push(x);
}
public void pop() {
}
public int top() {
}
public int getMin() {
}
}
// 辅助栈实现
class MinStack2 {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack2() {
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
if (!s2.empty()) {
if (s2.peek() > x) {
s2.push(x);
} else {
s2.push(s2.peek());
}
} else {
s2.push(x);
}
}
public void pop() {
s1.pop();
s2.pop();
}
public int top() {
return s1.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return s2.peek();
}
}
# 706. Design HashMap(设计哈希映射)
class MyHashMap {
int base = 769;
LinkedList[] data;
private int hash(int k) {
return k % base;
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyHashMap() {
data = new LinkedList[base];
}
/** value will always be non-negative. */
public void put(int key, int value) {
LinkedList list = data[hash(key)];
if (list == null) {
list = new LinkedList<Pair>();
data[hash(key)] = list;
}
Iterator<Pair> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Pair pair = iterator.next();
if (pair.k == key) {
pair.v = value;
return;
}
}
list.add(new Pair(key, value));
}
/** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or -1 if this map contains no mapping for the key */
public int get(int key) {
LinkedList list = data[hash(key)];
if (list == null) {
return -1;
}
Iterator<Pair> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Pair pair = iterator.next();
if (pair.k == key) {
return pair.v;
}
}
return -1;
}
/** Removes the mapping of the specified value key if this map contains a mapping for the key */
public void remove(int key) {
LinkedList list = data[hash(key)];
if (list == null) {
return;
}
Iterator<Pair> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Pair pair = iterator.next();
if (pair.k == key) {
iterator.remove();
// 不能直接使用remove(pair),会java.util.ConcurrentModificationException。需要添加return;
}
}
}
class Pair {
public Pair(int k, int v) {
this.k = k;
this.v = v;
}
int k;
int v;
}
}
/**
* Your MyHashMap object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyHashMap obj = new MyHashMap();
* obj.put(key,value);
* int param_2 = obj.get(key);
* obj.remove(key);
*/
# 54. Spiral Matrix(螺旋矩阵)
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] m) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int x = m[0].length;
int y = m.length;
// left, right, top, bottom
int l = 0, r = x-1, t = 0, b = y-1;
while (l <= r && t <= b) {
// top line
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
res.add(m[t][i]);
}
// right
for (int i = t+1; i <= b; i++) {
res.add(m[i][r]);
}
if (l < r && t < b) {
// bottom
for (int i = r-1; i > l; i--) {
res.add(m[b][i]);
}
// left
for (int i = b; i > t; i--) {
res.add(m[i][l]);
}
}
l++;
r--;
t++;
b--;
}
return res;
}
}
# 94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal(二叉树的中序遍历)
class Solution {
// 迭代
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode n) {
List<Integer> r = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<>();
while (!s.empty() || n != null) {
while (n != null) {
s.push(n);
n = n.left;
}
n = s.pop();
r.add(n.val);
n = n.right;
}
return r;
}
// 递归
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal2(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> r = new ArrayList<>();
recursive(root, r);
return r;
}
private void recursive(TreeNode n, List<Integer> r) {
if (n == null) return;
recursive(n.left, r);
r.add(n.val);
recursive(n.right, r);
}
}
# 59. Spiral Matrix II(螺旋矩阵 II)
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int[][] m = new int[n][n];
int n2 = n*n;
int l = 0, r = n-1, t = 0, b = n-1;
int w = 1;
while (l <= r && t <= b) {
// top line
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
m[t][i] = w;
w++;
}
// right
for (int i = t+1; i <= b; i++) {
m[i][r] = w;
w++;
}
if (l < r && t < b) {
// bottom
for (int i = r-1; i > l; i--) {
m[b][i] = w;
w++;
}
// left
for (int i = b; i > t; i--) {
m[i][l] = w;
w++;
}
}
l++;
r--;
t++;
b--;
}
return m;
}
}
# 103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal(二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历)
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
TreeNode n;
int cnt = 1;
boolean go = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> r = new ArrayList<>();
int tmp = 0;
while (cnt > 0) {
n = q.poll();
r.add(n.val);
if (n.left != null) {
q.offer(n.left);
tmp++;
}
if (n.right != null) {
q.offer(n.right);
tmp++;
}
cnt--;
}
cnt = tmp;
if (go) {
res.add(r);
} else {
Collections.reverse(r);
res.add(r);
}
go = !go;
}
return res;
}
}
# 2. Add Two Numbers(两数相加)
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode h = new ListNode();
ListNode n = h;
int up = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int a = 0, b = 0;
if (l1 != null) {
a = l1.val;
}
if (l2 != null) {
b = l2.val;
}
int v = a+b+up;
if (v >= 10) {
up = 1;
v -= 10;
} else {
up = 0;
}
n.next = new ListNode(v);
n = n.next;
if (l1 != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
if (up == 1) {
n.next = new ListNode(1);
}
return h.next;
}
}
# 328. Odd Even Linked List(奇偶链表)
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode h) {
ListNode odd = new ListNode();
ListNode even = new ListNode();
ListNode h2 = null;
boolean isOdd = true;
ListNode n = h;
while (n != null) {
if (isOdd) {
odd.next = n;
odd = odd.next;
} else {
if (h2 == null) {
h2 = n;
}
even.next = n;
even = even.next;
}
n = n.next;
isOdd = !isOdd;
}
odd.next = h2;
even.next = null;
return h;
}
}
# 115. Distinct Subsequences(不同的子序列)
class Solution {
// s[0:i] t[0:j]
// 前i个与前j个匹配 至少等于 前i+1个与前j个匹配 和 前+1个与前j+1个匹配
// dp[i][j] = d[i+1][j] + d[i+1][j+1];
// s[i:] t[j:]
// i到末尾与j到末尾序列匹配 至少等于 i+1到末尾与j到末尾匹配 和 i+1末尾与j+1末尾匹配
// dp[i][j] = d[i+1][j] + d[i+1][j+1];
public int numDistinct(String s, String t) {
int y = s.length();
int x = t.length();
int[][] dp = new int[y+1][x+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= x; i++) {
dp[y][i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= y; i++) {
dp[i][x] = 1;
}
for (int i = y-1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = x-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (s.charAt(i) == t.charAt(j)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j] + dp[i+1][j+1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j];
}
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}
# 116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node(填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针)
class Solution {
// bfs
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) return null;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
Node n = root;
q.offer(n);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node tmp = null;
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
n = q.poll();
n.next = tmp;
tmp = n;
if (n.right != null) q.offer(n.right);
if (n.left != null) q.offer(n.left);
}
}
return root;
}
}
# 230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
class Solution {
TreeNode res = null;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
recusive(root, k);
return res.val;
}
public int recusive(TreeNode n, int k) {
if (n == null) {
return k;
}
// left
k = recusive(n.left, k);
// mid myself
k--;
if (res == null && k == 0) {
res = n;
}
// right
k = recusive(n.right, k);
return k;
}
}
# 200. Number of Islands(岛屿数量)
class Solution {
int col;
int row;
int cnt = 0;
public int numIslands(char[][] g) {
col = g[0].length;
row = g.length;
// System.out.println("col:"+col+"row:"+row);
for (int y = 0; y < row; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < col; x++) {
// System.out.println("g[y][x]::y"+y+"x"+x+";;;;val:"+g[y][x]);
if (g[y][x] == '1') {
cnt++;
bfs(g, x, y);
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
private void bfs(char[][] n, int x, int y) {
// base condtion
if (x > col-1 || y > row-1 || y < 0 || x < 0) {
return;
}
if (n[y][x] == '2' || n[y][x] == '0') {
return;
}
// process
if (n[y][x] == '1') {
n[y][x] = '2';
}
// up
bfs(n, x, y-1);
// down
bfs(n, x, y+1);
// left
bfs(n, x-1, y);
// right
bfs(n, x+1, y);
}
}
# 160. 相交链表
同剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode A, ListNode B) {
ListNode a = A;
ListNode b = B;
boolean _a = true;
boolean _b = true;
while (a != b) {
if (a.next == null && _a) {
a = B;
_a = false;
} else {
a = a.next;
}
if (b.next == null && _b) {
b = A;
_b = false;
} else {
b = b.next;
}
}
return a;
}
}
官解的更优写法:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode ha = headA, hb = headB;
if (ha == null || hb == null) return null;
while (ha != hb) {
ha = ha == null ? headB : ha.next;
hb = hb == null ? headA : hb.next;
}
return ha;
}
}
使用双向链表linkedList,先存储两条链表,然后从后回放,链表要相交,则后面一定相等:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode ha = headA, hb = headB;
LinkedList<ListNode> qa = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<ListNode> qb = new LinkedList<>();
while (ha != null) {
qa.offerLast(ha);
ha = ha.next;
}
while (hb != null) {
qb.offerLast(hb);
hb = hb.next;
}
ListNode pre = null;
while (qa.size() != 0 && qb.size() != 0) {
ListNode qaN = qa.pollLast();
if (qaN == qb.pollLast()) {
pre = qaN;
} else {
return pre;
}
}
return pre;
}
}
使用栈:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Stack<ListNode> sa = new Stack<>();
Stack<ListNode> sb = new Stack<>();
while (headA != null) {
sa.push(headA);
headA = headA.next;
}
while (headB != null) {
sb.push(headB);
headB = headB.next;
}
ListNode pre = null;
while (!sa.empty() && !sb.empty()) {
ListNode ta = sa.pop();
ListNode tb = sb.pop();
// System.out.println("ta:"+ta.val+"; tb:"+tb.val);
if (ta == tb) {
pre = ta;
} else {
return pre;
}
}
return pre;
}
}
# 92. Reverse Linked List II(反转链表 II)
class Solution {
// brute force
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode h, int l, int r) {
if (h.next == null) return h;
int gap = r - l;
ListNode pre = new ListNode();
pre.next = h;
ListNode c1 = h;
ListNode c2 = h;
h = pre;
while (l > 1 && c1 != null) {
pre = c1;
c1 = c1.next;
l--;
}
c2 = c1;
ListNode next = null;
while (gap > 0 && c2.next != null) {
next = c2.next;
c2.next = next.next;
next.next = c1;
pre.next = next;
c1 = next;
gap--;
}
return h.next;
}
}
# 22. Generate Parentheses(括号生成)
class Solution {
// dfs
int n;
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
this.n = n;
dfs("", "(", 1, 0);
return res;
}
private void dfs(String s, String p, int l, int r) {
s = s + p;
if (r > l) {
return;
}
if (s.length() == n*2) {
if (l == r) {
res.add(s);
}
return;
}
// System.out.println(s);
dfs(s, "(", l+1, r);
dfs(s, ")", l, r+1);
}
}
# 46. Permutations(全排列)
class Solution {
// 递归树结构图
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] n) {
boolean[] used = new boolean[n.length];
recursive(new ArrayList<>(), used, n);
return res;
}
private void recursive(List<Integer> list, boolean[] used, int[] n) {
if (list.size() >= n.length) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < used.length; j++) {
if (!used[j]) {
used[j] = true;
list.add(n[j]);
recursive(list, used, n);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
used[j] = false;
}
}
}
}
一个月后再做,回溯解法:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
LinkedList<Integer> track = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];
recur(nums, track, used);
return res;
}
// track的类型改为ArrayList,因为之前的LinkedList是链表结构,将其转ArrayList的转换性能地下。建议都保持一致类型即可。
private void recur(int[] nums, LinkedList<Integer> track, boolean[] used) {
if (track.size() == nums.length) {
res.add(new LinkedList(track));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 使用hash数组标记法来判断是否存在比contains效率更高,因为contains需要遍历。
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
track.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
recur(nums, track, used);
// 由于i+1需要用到完整数组,所以要给他还原回去。
track.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
# 78. Subsets(子集)
class Solution {
// @jesse 画递归树
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
dfs(nums, 0);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums, int start) {
if (start > nums.length) {
return;
} else {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
}
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
list.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, i+1);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
}
}
// @国际站
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> output = new ArrayList();
output.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
for (int num : nums) {
List<List<Integer>> newSubsets = new ArrayList();
for (List<Integer> curr : output) {
newSubsets.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(curr) {{
add(num);
}});
}
for (List<Integer> curr : newSubsets) {
output.add(curr);
}
}
return output;
}
}
class Solution {
// @题解
// [[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
recursive(nums, 0);
return res;
}
public void recursive(int[] nums, int i) {
if (i == nums.length) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
list.add(nums[i]);
recursive(nums, i+1);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
recursive(nums, i+1);
}
}
# 79. Word Search(单词搜索)
class Solution {
// brute force
boolean[][] used;
public boolean exist(char[][] b, String w) {
for (int y = 0; y < b.length; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < b[0].length; x++) {
used = new boolean[b.length][b[0].length];
if (recursive(x, y, b, w, 0)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean recursive(int x, int y, char[][] b, String w, int cnt) {
// base condition
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= b[0].length || y >= b.length || used[y][x]) {
return false;
}
used[y][x] = true;
// System.out.println("x:"+x+";y:"+y);
// System.out.println("charAt:"+cnt+";val:"+w.charAt(cnt)+";char:"+b[y][x]);
// System.out.println("used:"+used[y][x]);
if (b[y][x] != w.charAt(cnt)) {
used[y][x] = false;
return false;
}
if (cnt == w.length()-1) {
return true;
}
// up
boolean res = recursive(x, y-1, b, w, cnt+1)
// down
|| recursive(x, y+1, b, w, cnt+1)
// left
|| recursive(x-1, y, b, w, cnt+1)
// right
|| recursive(x+1, y, b, w, cnt+1);
used[y][x] = false;
return res;
}
}
# 1603. Design Parking System(设计停车系统)
class ParkingSystem {
int[] map = new int[4];
public ParkingSystem(int big, int medium, int small) {
map[1] = big;
map[2] = medium;
map[3] = small;
}
public boolean addCar(int carType) {
int cnt = map[carType];
if (cnt > 0) {
cnt--;
map[carType] = cnt;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// public ParkingSystem(int big, int medium, int small) {
// map.put(1, big);
// map.put(2, medium);
// map.put(3, small);
// }
//
// public boolean addCar(int carType) {
// int cnt = map.get(carType);
// if (cnt > 0) {
// cnt--;
// map.put(carType, cnt);
// return true;
// }
// return false;
// }
}
# 55. 跳跃游戏
暴力解,耗时击败10%:
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
boolean[] dp = new boolean[n];
dp[0] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (dp[i]) {
int k = nums[i], j = 1;
while (j <= k && i+j < n) {
dp[i+j] = true;
j++;
}
}
}
return dp[n-1];
}
}
动态规划
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] n) {
// i + n[i] >= n.length
int len = n.length;
if (len < 2) return true;
int max = 1+n[0];
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
max = Math.max(i+1+n[i], max);
if (i+1+n[i] >= len) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
动态规划写法二:
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (max >= i) {
max = Math.max(max, i+nums[i]);
}
}
return max >= n-1;
}
}
几个月后再次写
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, end = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i <= end && end < n; i++) {
int d = i + nums[i];
end = d > end ? d : end;
}
return end >= n-1;
}
}
# 62. 不同路径
class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
// f(x,y) = f(x,y-1) + f(x-1,y)
int[][] u = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
u[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
u[0][i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
u[i][j] = u[i][j-1] + u[i-1][j];
}
}
return u[m-1][n-1];
}
}
代码更简洁的写法:
class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[][] dp = new int[m+1][n+1];
dp[1][1] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) continue;
dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j+1] + dp[i+1][j];
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}
# 150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation(逆波兰表达式求值)
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] ts) {
Stack<String> s = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < ts.length; i++) {
if (isOper(ts[i])) {
String back = s.pop();
String front = s.pop();
int result = calculation(ts[i], front, back);
s.push(String.valueOf(result));
} else {
s.push(ts[i]);
}
}
return Integer.valueOf(s.pop());
}
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
{
set.add("+");
set.add("-");
set.add("*");
set.add("/");
}
private boolean isOper(String c) {
return set.contains(c);
}
private int calculation(String oper, String f, String b) {
int res = 0;
switch (oper) {
case "+": res = Integer.valueOf(f) + Integer.valueOf(b);
break;
case "-": res = Integer.valueOf(f) - Integer.valueOf(b);
break;
case "*": res = Integer.valueOf(f) * Integer.valueOf(b);
break;
case "/": res = Integer.valueOf(f) / Integer.valueOf(b);
break;
default:
}
return res;
}
}
# 322. 零钱兑换
public class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int n = coins.length;
int[] dp = new int[amount+1];
Arrays.fill(dp, amount+1);
dp[0] = 0;
// i is amount
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i-coins[j] >= 0) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i-coins[j]]+1);
}
}
}
if (dp[amount] == amount+1){
return -1;
}
return dp[amount];
}
}
动态规划:
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int n = coins.length;
int[] dp = new int[amount+1];
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
dp[i] = -1;
for (int j = n-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (i >= coins[j] && dp[i-coins[j]] != -1) {
dp[i] = dp[i] == -1 ? dp[i-coins[j]] + 1 : Math.min(dp[i], dp[i-coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount];
}
}
// 超时 @jesse
class Solution {
// dp+贪心
// [10,7,1] 15 => 10+1+1+1+1 | 7+7+1
// [10,8,7,1] 25 => 10+10+1+1... | 10+8+7
// 递归树
// 剪枝:1.同level下后续节点的子节点是从同值开始遍历 2.记录最小深度,如果深度大于前面最小深度,即此时最小深度为最少硬币个数
int min = 999999;
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
if (amount <= 0)
return 0;
coins = IntStream.of(coins).boxed().sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder()).mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(coins));
for (int i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
recursive(coins, i, amount, 1);
}
if (min == 999999) return -1;
return min;
}
private void recursive(int[] cs, int i, int remainder, int deep) {
if (i >= cs.length) return;
if (cs[i] > remainder) {
return;
}
remainder -= cs[i];
// System.out.println("remainder:"+remainder+";cs[i]:"+cs[i]);
if (remainder <= 0) {
// System.out.println("deep:"+deep+";min:"+min);
if (deep < min) {
min = deep;
}
return;
}
for (int j = i; j < cs.length; j++) {
recursive(cs, j, remainder, deep+1);
}
}
}
dfs爆搜,未考虑缓存处理,超时:
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
Arrays.sort(coins);
dfs(coins, amount, 0, 0, coins.length-1);
return res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res;
}
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private void dfs(int[] coins, int t, int sum, int cnt, int start) {
// System.out.println("coins:"+Arrays.toString(coins)+"; t:"+t+"; sum:"+sum+"; cnt:"+cnt+"; start"+start);
if (sum == t) {
res = Math.min(res, cnt);
return;
}
for (int i = start; i >= 0; i--) {
if (sum + coins[i] > t) continue;
dfs(coins, t, sum+coins[i], cnt+1, i);
}
}
}
修改爆搜,递归方法的签名支持返回结果,有利于接下来缓存结果,避免重复计算,与之前复杂度未有变化,无法ac:
class Solution {
int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int res = dfs(coins, amount);
return res == INF ? -1 : res;
}
private int dfs(int[] coins, int t) {
if (t == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (t < 0) {
return -1;
}
int res = INF;
for (int i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
if (t-coins[i] >= 0) {
res = Math.min(res, dfs(coins, t-coins[i])+1);
}
}
return res;
}
}
继续修改爆搜,使用cache,成功ac:
class Solution {
int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int[] cache;
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
cache = new int[amount+1];
int res = dfs(coins, amount);
return res == INF ? -1 : res;
}
private int dfs(int[] coins, int t) {
if (t == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (t < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (cache[t] != 0) {
return cache[t];
}
int res = INF;
for (int i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
int rem = t-coins[i];
if (rem >= 0) {
res = Math.min(res, dfs(coins, rem)+1);
}
}
cache[t] = res;
return res;
}
}
通过缓存结果成功ac后,可以看出因为递归函数的结果计算存在重复,所以使用其参数(剩余的和)作为key,将结果缓存,就能大大降低计算时间:
class Solution {
int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
// 根据递归的dfs函数看出,结果跟剩余的和相关(t)
// define dp array 代表剩余i的零钱,最少需要dp[i]个硬币
// 动归方程:dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i]
int[] dp = new int[amount+1];
// 默认本来就是0,这里显示初始化一下是为了表示它的意义:在剩余金额为0的时候,需要的最少硬币是0枚
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
int res = INF;
for (int c : coins) {
if (i-c >= 0) {
res = Math.min(res, dp[i-c]+1);
}
}
dp[i] = res;
}
return dp[amount] == INF ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
}
# 300. 最长递增子序列
// O(nlogn)
class Solution {
// [10,9,2,5,4,7,3,6,101,18] 18->dp[]{2,3,7,101}
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// dp[i] 长度为i的子序列的末尾值
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
// 最长子序列的长度
int len = 1;
dp[1] = 999999;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// System.out.println("len:"+len);
// System.out.println("dp:"+Arrays.toString(dp));
if (nums[i] > dp[len]) {
len++;
dp[len] = nums[i];
} else {
binarySearchAndReplace(dp, len, nums[i]);
}
}
return len;
}
private void binarySearchAndReplace(int[] dp, int mi, int v) {
int l = 1;
int r = mi;
int p = 0;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
if (dp[m] > v) {
r = m - 1;
} else if (dp[m] < v) {
p = m;
l = m + 1;
} else {
return;
}
}
dp[p+1] = v;
}
}
可读性更好的代码:
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
int right = 1;
dp[1] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
right = Math.max(right, replace(dp, 1, right, nums[i]));
}
return right;
}
public int replace(int[] dp, int left, int right, int t) {
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + ((right-left)>>1);
if (t > dp[mid]) {
left = mid+1;
} else {
right = mid-1;
}
}
dp[left] = t;
return left;
}
}
动态规划:
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
for (int j = i-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j]+1);
}
}
max = Math.max(max, dp[i]);
}
return max;
}
}
# 73. Set Matrix Zeroes(矩阵置零)
class Solution {
// O(2m+2n+2mn)
public void setZeroes(int[][] m) {
// 检查上和左边,记录是否存在0
// 遍历数组,遇0,将其m[y][0],m[0][x]置0
// 二次遍历数组,遇非0,m[y][0],m[0][x]如果存在0,则将其置0
int x = m[0].length;
int y = m.length;
boolean xf = false;
boolean yf = false;
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
if (m[0][i] == 0) {
xf = true;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < y; i++) {
if (m[i][0] == 0) {
yf = true;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < y; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < x; j++) {
if (m[i][j] == 0) {
m[i][0] = 0;
m[0][j] = 0;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < y; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < x; j++) {
if (m[i][j] != 0) {
if (m[i][0] == 0 || m[0][j] == 0) {
m[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
if (xf) {
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
m[0][i] = 0;
}
}
if (yf) {
for (int i = 0; i < y; i++) {
m[i][0] = 0;
}
}
}
}
# 297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
相同题:剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树 (opens new window)
这应该是我看题解做出来的:
public class Codec {
// bfs
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
if (root == null) {
return res.toString();
}
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
TreeNode n;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
while (size > 0) {
n = q.poll();
if (n != null) {
res.append(n.val);
q.offer(n.left);
q.offer(n.right);
} else {
res.append("null");
}
res.append(",");
size--;
}
}
System.out.println("serialize:"+res.toString());
return res.toString();
}
public TreeNode deserialize(String s) {
String[] nums = s.split(",");
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList(nums));
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
if ("".equals(list.get(0)) || "null".equals(list.get(0))) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(list.get(0)));
q.offer(root);
list.remove(0);
TreeNode n;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
while (size > 0) {
n = q.poll();
TreeNode left;
if ("".equals(list.get(0)) || "null".equals(list.get(0))) {
left = null;
list.remove(0);
} else {
left = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(list.get(0)));
list.remove(0);
q.offer(left);
}
n.left = left;
TreeNode right;
if ("".equals(list.get(0)) || "null".equals(list.get(0))) {
right = null;
list.remove(0);
} else {
right = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(list.get(0)));
list.remove(0);
q.offer(right);
}
n.right = right;
size--;
}
}
return root;
}
}
一个月后,看labuladong小抄后,再做。 前序遍历实现:
public class Codec {
private static final String SEP = ",";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
recursive(root, sb);
return sb.delete(sb.length()-1, sb.length()).toString();
}
private void recursive(TreeNode node, StringBuilder sb) {
if (node == null) {
sb.append("#").append(SEP);
return;
}
// 前序遍历,先将root的值加入String
sb.append(node.val).append(SEP);
recursive(node.left, sb);
recursive(node.right, sb);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
LinkedList<String> nodes = new LinkedList<>();
for (String s : data.split(SEP)) {
nodes.addLast(s);
}
return recursive(nodes);
}
private TreeNode recursive(LinkedList<String> nodes) {
if (nodes.size() <= 0) {
return null;
}
// 前序遍历的第一个节点一定为root节点
TreeNode root = null;
String node = nodes.removeFirst();
if (!node.equals("#")) {
root = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(node));
// left
root.left = recursive(nodes);
// right
root.right = recursive(nodes);
}
return root;
}
}
后序遍历实现:
public class Codec {
private static final String SEP = ",";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
recursive(root, sb);
return sb.delete(sb.length()-1, sb.length()).toString();
}
private void recursive(TreeNode node, StringBuilder sb) {
if (node == null) {
sb.append("#").append(SEP);
return;
}
recursive(node.left, sb);
recursive(node.right, sb);
// 后序遍历
sb.append(node.val).append(SEP);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
LinkedList<String> nodes = new LinkedList<>();
for (String s : data.split(SEP)) {
nodes.addLast(s);
}
return recursive(nodes);
}
private TreeNode recursive(LinkedList<String> nodes) {
if (nodes.size() <= 0) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = null;
// 后序遍历,root是后面第一个
String node = nodes.removeLast();
if (!node.equals("#")) {
root = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(node));
// 后序遍历,先right,后left,不理解一画图就明白了。
root.right = recursive(nodes);
root.left = recursive(nodes);
}
return root;
}
}
反序列化时,中序遍历由于无法确定root节点位置,因此无法构造二叉树:
public class Codec {
private static final String SEP = ",";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
recursive(root, sb);
return sb.delete(sb.length()-1, sb.length()).toString();
}
private void recursive(TreeNode node, StringBuilder sb) {
if (node == null) {
sb.append("#").append(SEP);
return;
}
recursive(node.left, sb);
// 中序遍历
sb.append(node.val).append(SEP);
recursive(node.right, sb);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
// 无法找到root节点
}
}
层级遍历:
层级遍历有两种反序列化写法,逻辑其实是一样的,都是将上一层节点存入queue中,在遍历到层是,取出来,为其装上左右腿(node.left, node.right)。 这是自己写的:
public class Codec {
private static final String SEP = ",";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if (node == null) {
sb.append("#").append(SEP);
} else {
sb.append(node.val).append(SEP);
q.offer(node.left);
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
return sb.delete(sb.length()-1, sb.length()).toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
LinkedList<String> nodes = new LinkedList<>();
for (String s : data.split(SEP)) {
nodes.addLast(s);
}
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
String first = nodes.removeFirst();
if (first.equals("#")) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(first));
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if (node != null) {
// 加入到
String left = nodes.removeFirst();
String right = nodes.removeFirst();
if (!left.equals("#")) {
node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(left));
}
if (!right.equals("#")) {
node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(right));
}
q.offer(node.left);
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
这是参考labuladong的方法:
public class Codec {
private static final String SEP = ",";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if (node == null) {
sb.append("#").append(SEP);
} else {
sb.append(node.val).append(SEP);
q.offer(node.left);
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
return sb.delete(sb.length()-1, sb.length()).toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] nodes = data.split(SEP);
if (nodes[0].equals("#")) {
return null;
}
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(nodes[0]));
q.offer(root);
// 第一个一定有值时,i不停后移
for (int i = 1; i < nodes.length; ) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
String left = nodes[i++];
if (!left.equals("#")) {
node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(left));
q.offer(node.left);
}
String right = nodes[i++];
if (!right.equals("#")) {
node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(right));
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}
再过2个月后,凭感觉做出来了,但是忘记其他方法怎么做的了 go解法:
import "fmt"
type Codec struct {
}
func Constructor() Codec {
c := Codec{}
return c
}
// Serializes a tree to a single string.
func (this *Codec) serialize(root *TreeNode) string {
res := ""
serialize(root, &res)
// fmt.Println(res[1:])
return res[1:]
}
func serialize(n *TreeNode, res *string) {
if n == nil {
*res = *res + ",#"
return
}
*res = *res + "," + strconv.Itoa(n.Val)
serialize(n.Left, res)
serialize(n.Right, res)
}
// Deserializes your encoded data to tree.
func (this *Codec) deserialize(data string) *TreeNode {
if data == "" {
return nil
}
arr := strings.Split(data, ",")
// fmt.Println(arr)
return deserialize(&arr)
}
func deserialize(s *[]string) *TreeNode {
// fmt.Println(len(*s))
if len(*s) == 0 {
return nil
}
if (*s)[0] == "#" {
*s = (*s)[1:]
return nil
}
v,_ := strconv.Atoi((*s)[0])
// fmt.Println(v)
n := TreeNode{v, nil, nil}
*s = (*s)[1:]
n.Left = deserialize(s)
n.Right = deserialize(s)
return &n
}
过一年,使用层序遍历实现,比之前写得在完成度上看是更好的。
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.valueOf(root.val)).append(",");
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
TreeNode poll = q.poll();
if (poll.left == null) {
res.append("#");
} else {
res.append(String.valueOf(poll.left.val));
q.offer(poll.left);
}
res.append(",");
if (poll.right == null) {
res.append("#");
} else {
res.append(String.valueOf(poll.right.val));
q.offer(poll.right);
}
res.append(",");
}
}
return res.deleteCharAt(res.length()-1).toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if (data == null || data.length() == 0) return null;
String[] split = data.split(",");
int index = 1;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(split[0]));
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty() && index < split.length) {
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
TreeNode poll = q.poll();
String left = split[index++];
String right = split[index++];
if (!left.equals("#")) {
poll.left = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(left));
q.offer(poll.left);
}
if (!right.equals("#")) {
poll.right = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(right));
q.offer(poll.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
# 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1)(常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素)
同:剑指 Offer II 030. 插入、删除和随机访问都是 O(1) 的容器
class RandomizedSet {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Random random = new Random();
public RandomizedSet() {
}
public boolean insert(int val) {
if (map.containsKey(val)) return false;
map.put(val, list.size());
list.add(val);
return true;
}
public boolean remove(int val) {
if (!map.containsKey(val)) return false;
int index = map.get(val);
int n = list.size();
Integer last = list.get(n - 1);
list.set(index, last);
list.remove(n - 1);
map.put(last, index);
map.remove(val);
return true;
}
public int getRandom() {
return list.get(random.nextInt(list.size()));
}
}
# 202. 快乐数
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
int slow = n;
int fast = cal(n);
while (slow != fast) {
slow = cal(slow);
fast = cal(cal(fast));
}
return slow == 1;
}
private int cal(int n){
int res = 0;
while (n >= 10) {
int remainder = n % 10;
n = n / 10;
res += remainder * remainder;
}
res += n*n;
return res;
}
}
使用set看是否重复:
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
while (n != 1) {
if (!set.add(n)) {
return false;
}
n = func(n);
}
return true;
}
private int func(int n) {
String s = String.valueOf(n);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int tmp = s.charAt(i) - '0';
res += (tmp * tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
# 172. Factorial Trailing Zeroes(阶乘后的零)
class Solution {
public int trailingZeroes(int n) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 5; i <= n; i+=5) {
int tmp = i;
while (tmp % 5 == 0) {
tmp = tmp / 5;
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
}
# 171. Excel表列序号
class Solution {
public int titleToNumber(String s) {
int n = s.length();
int res = 0;
int digit = 1;
for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
res += digit * (s.charAt(i) - 'A' + 1);
digit *= 26;
}
return res;
}
}
go解法: 思路和代码偏复杂,可以从前向后遍历,不一定要从低位计算:
import "math"
func titleToNumber(s string) (res int) {
l := len(s)
n := l-1
t := 0
for n >= 0 {
cur := int(s[n]-'A')+1
res += powInt(26, t) * cur
s = s[0:n]
t++
n--
}
return
}
func powInt(x, y int) int {
return int(math.Pow(float64(x), float64(y)))
}
【优化解】从高位计算,代码简单:
func titleToNumber(ss string) (res int) {
for _, n := range ss {
res = res * 26 + (int(n-'A')+1)
}
return
}
# 50. Pow(x, n)
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
// x^n = x^n/2 * x^n/2
long N = n;
if (N == 0) {
return 1d;
} else if (N < 0) {
return 1d / f(x, -N);
} else {
return f(x, N);
}
}
private double f(double x, long N) {
if (N <= 1) {
return x;
}
double tmp = f(x, N/2);
if (N % 2 != 0) {
return tmp * tmp * x;
} else {
return tmp * tmp;
}
}
}
# 3. 无重复字符的最长子串
记录下标位置是最好的做法:
class Solution {
// 滑动窗口
// map记录窗口中的内容,value为数组下标位置,检测是否重复,重复则将l置为重复下标+1处
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int len = 0;
int n = s.length();
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int l = 0;
int r = 0;
while (r < n) {
if (map.containsKey(s.charAt(r))) {
int tmp = map.get(s.charAt(r)) + 1;
while (l < tmp) {
map.remove(s.charAt(l));
l++;
}
len = Math.max(len, r-l+1);
} else {
map.put(s.charAt(r), r);
r++;
len = Math.max(len, r-l);
}
// System.out.println("r: "+r+";l: "+l+" len: "+len);
}
return len;
}
}
2021-08-29再做:
滑动窗口:
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int n = s.length();
Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
int max = 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < n) {
char cur = s.charAt(right);
if (!set.contains(cur)) {
set.add(cur);
right++;
max = Math.max(max, right-left);
} else {
while (left <= right && set.contains(cur)) {
set.remove(s.charAt(left));
left++;
}
}
}
return max;
}
}
再优化后:
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int n = s.length();
Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
int max = 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < n) {
char cur = s.charAt(right);
if (!set.contains(cur)) {
set.add(cur);
right++;
max = Math.max(max, right-left);
} else {
set.remove(s.charAt(left));
left++;
}
}
return max;
}
}
# 5. 最长回文子串
class Solution {
// 动态规划 @liweiwei1419 按同样思路,边界条件处理不好
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
// dp[i][j] 代表i到j是否为回文子串
// f(i, j) = f(i+1, j-1) & (s[i] == s[j])
int mLen = 1;
int begin = 0;
int n = s.length();
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i][i] = true;
}
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {
if (j - i < 3) {
dp[i][j] = true;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j-1];
}
} else {
dp[i][j] = false;
}
if (dp[i][j] && j-i+1 > mLen) {
mLen = j-i+1;
begin = i;
}
}
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(dp));
return s.substring(begin, begin+mLen);
}
}
重刷,写动态规划,代码编写上更轻松了,代码也更好看了,但是仍然没法直接看出解决思路,需要仔细验证才做出来,说明还是没有明白这道题的关键:
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
int n = s.length();
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i][i] = true;
}
int maxLen = 1;
String res = s.substring(0, 1);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {
dp[i][j] = i+1==j ? true : dp[i+1][j-1];
}
if (dp[i][j] && j-i+1 > maxLen) {
res = s.substring(i, j+1);
maxLen = j-i+1;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
# 334. Increasing Triplet Subsequence(递增的三元子序列)
class Solution {
// @题解
public boolean increasingTriplet(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n < 3) {
return false;
}
int low = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int mid = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// System.out.println("low:"+low+"; mid:"+mid);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] <= low) {
low = nums[i];
} else if (nums[i] <= mid) {
mid = nums[i];
}else if (nums[i] > mid) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
# 456. 132 模式
// 单调栈
class Solution {
public boolean find132pattern(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n < 3) return false;
// i j k; i<j; j>k; i<k;
int k = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Stack<Integer> ms = new Stack<>();
for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (k > nums[i]) {
return true;
}
// if stack empty or stack pop elem >= nums[i]; put int
if (ms.empty() || ms.peek() >= nums[i]) {
ms.push(nums[i]);
} else {
// stack is not empty & stack pop el < nums[i];
while (!ms.empty() && ms.peek() < nums[i]) {
k = Math.max(k, ms.pop());
}
}
ms.push(nums[i]);
}
return false;
}
}
重刷,还是做不出,仍然是看答案解,这题算是单调栈中较难的了
class Solution {
public boolean find132pattern(int[] nums) {
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<>();
int n = nums.length, INF = Integer.MIN_VALUE, k = INF;
for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s.empty()) {
s.push(nums[i]);
continue;
}
if (!s.empty() && k > nums[i]) {
return true;
}
while (!s.empty() && nums[i] > s.peek()) {
k = Math.max(k, s.pop());
}
s.push(nums[i]);
}
return false;
}
}
# 82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II(删除排序链表中的重复元素 II)
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dumy = new ListNode();
dumy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dumy;
ListNode c1 = head;
ListNode c2 = head;
if (c2 == null) return null;
while (c2.next != null) {
if (c2.next != null && c2.val == c2.next.val) {
while (c2.next != null && c2.val == c2.next.val) {
c2 = c2.next;
}
if (c2.next == null) {
pre.next = null;
} else {
// c2.val != c2.next.val
c2 = c2.next;
c1 = c2;
pre.next = c2;
}
} else {
pre = pre.next;
c1 = c1.next;
c2 = c2.next;
}
}
return dumy.next;
}
}
重刷时,发现自己思路更清晰,写出的代码更加简洁了:
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode s = new ListNode(-1000, head);
ListNode p = s, c = s.next;
while (c != null && c.next != null) {
if (c.next.val != c.val) {
if (p.next != c) {
p.next = c.next;
} else {
p = p.next;
}
}
c = c.next;
}
if (p.next != c) p.next = null;
return s.next;
}
}
# 371. 两整数之和
class Solution {
public int getSum(int a, int b) {
while (b!=0) {
int t1 = a^b;
int t2 = (a&b)<<1;
a = t1;
b = t2;
}
return b | a;
}
}
朴素解法:
class Solution {
public int getSum(int a, int b) {
int res = 0, rem = 0;
for (int offset = 0; offset < 32; offset++) {
int ca = (a >> offset) & 1;
int cb = (b >> offset) & 1;
int c = 0;
if ((ca ^ cb) == 1) {
c = 1;
if (rem == 1) {
c = 0;
}
} else {
if ((ca & cb) == 1) {
if (rem == 1) {
c = 1;
} else {
rem = 1;
}
} else {
if (rem == 1) {
c = 1;
rem = 0;
}
}
}
res = res | (c << offset);
}
return res;
}
}
# 83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dumy = new ListNode();
dumy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dumy;
ListNode c1 = head;
ListNode c2 = head;
if (c2 == null) return null;
while (c2.next != null) {
if (c2.next != null && c2.val == c2.next.val) {
while (c2.next != null && c2.val == c2.next.val) {
c2 = c2.next;
}
if (c2.next == null) {
c1.next = null;
} else {
// c2.val != c2.next.val
c1 = c2;
pre.next = c2;
}
} else {
pre = pre.next;
c1 = c1.next;
c2 = c2.next;
}
}
return dumy.next;
}
}
# 69. Sqrt(x)(x 的平方根)
class Solution {
// a<=(a/2)^2 -> 4a<=a^2 -> a=>4 或 a<=0
// 10的一半5,10<=25
// 100/2=50: 100<=2500; 50/2=25: 100<=625; 25/2=12: 100<=144; 12/2=6: 36>100; 12+6/2=9: 81>100; 9+12/2=10; 100=100;
public int mySqrt(int x) {
long l = 0;
long r = x;
while (l < r) {
long mid = (l+r+1)/2;
long mul = mid*mid;
if (x < mul) {
r = mid-1;
} else {
l = mid;
}
}
return (int)l;
}
}
# 61. Rotate List(旋转链表)
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null || k == 0) {
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
int cnt = 1;
int kk = k;
while (fast.next != null) {
cnt++;
fast = fast.next;
if (k > 0) {
k--;
} else {
slow = slow.next;
}
}
if (k != 0) {
k = kk % cnt;
slow = head;
fast = head;
if (k == 0) {
return head;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
if (k > 0) {
k--;
} else {
slow = slow.next;
}
}
}
fast.next = head;
head = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
return head;
}
}
# 173. Binary Search Tree Iterator(二叉搜索树迭代器)
class BSTIterator {
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<>();
TreeNode n = null;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
n = root;
while (n != null) {
s.push(n);
n = n.left;
}
}
public int next() {
int res = 0;
while (n != null) {
s.push(n);
n = n.left;
}
if (!s.empty()) {
n = s.pop();
res = n.val;
n = n.right;
}
return res;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return !s.empty() || n != null;
}
}
# 347. Top K Frequent Elements(前 K 个高频元素)
class Solution {
// [1,1,1,2,2,3] 2
// [4,1,-1,2,-1,2,3] 2
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int[] res = new int[k];
Heap h = new Heap(k);
int n = nums.length;
Pair curr = null;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (curr == null) {
curr = new Pair(nums[i], 1);
}
// System.out.println("curr:"+curr);
if (i+1 < n && nums[i] != nums[i+1]) {
// 存在下一个 && 与下一个不相等
if (k > 0) {
k--;
h.insert(curr);
} else {
// 与堆顶比较
if (curr.cnt > h.a[1].cnt) {
h.remove();
h.insert(curr);
}
}
curr = null;
} else if (i+1 >= n){
// 不存在下一个
if (curr != null) {
if (k > 0) {
k--;
h.insert(curr);
} else {
// 与堆顶比较
if (curr.cnt > h.a[1].cnt) {
h.remove();
h.insert(curr);
}
}
}
} else {
// 或 与下一个相等
curr.cnt++;
}
}
// System.out.println("h.count:"+h.count);
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(h.a));
for (int i = 1; i <= h.count; i++) {
res[i-1] = h.a[i].key;
}
return res;
}
class Pair {
public Pair(int key, int cnt){
this.key = key;
this.cnt = cnt;
}
int key;
int cnt;
public String toString(){
return "key:"+key+"; cnt:"+cnt;
}
}
class Heap {
private Pair[] a;
// 最大数据个数K
private int n;
// 已经存储的最大个数
private int count;
public Heap(int cap) {
a = new Pair[cap+1];
n = cap;
count = 0;
}
public void insert(Pair p) {
if (count >= n) {
return;
}
++count;
a[count] = p;
int i = count;
while (i/2 > 0 && a[i].cnt < a[i/2].cnt) {
swap(a, i, i/2);
i = i/2;
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public void remove() {
if (count == 0) return;
a[1] = a[count];
--count;
heapify(a, count, 1);
}
public void heapify(Pair[] a, int cc, int i) {
while (true) {
int maxPos = i;
if (i*2 <= cc && a[i].cnt > a[i*2].cnt) maxPos = i*2;
if (i*2+1 <= cc && a[maxPos].cnt > a[i*2+1].cnt) maxPos = i*2+1;
if (maxPos == i) break;
swap(a, i, maxPos);
i = maxPos;
}
}
public void swap(Pair[] a, int source, int target) {
Pair tmp = a[source];
a[source] = a[target];
a[target] = tmp;
}
}
}
# 215. Kth Largest Element in an Array(数组中的第K个最大元素)
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
Heap h = new Heap(k);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (k > 0) {
k--;
h.insert(nums[i]);
} else {
if (nums[i] >= h.a[1]) {
h.remove();
h.insert(nums[i]);
}
}
}
return h.a[1];
}
class Heap {
private int[] a;
// 最大数据个数K
private int n;
// 已经存储的最大个数
private int count;
public Heap(int cap) {
a = new int[cap+1];
n = cap;
count = 0;
}
public void insert(int p) {
if (count >= n) {
return;
}
++count;
a[count] = p;
int i = count;
while (i/2 > 0 && a[i] < a[i/2]) {
swap(a, i, i/2);
i = i/2;
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public void remove() {
if (count == 0) return;
a[1] = a[count];
--count;
heapify(a, count, 1);
}
public void heapify(int[] a, int cc, int i) {
while (true) {
int maxPos = i;
if (i*2 <= cc && a[i] > a[i*2]) maxPos = i*2;
if (i*2+1 <= cc && a[maxPos] > a[i*2+1]) maxPos = i*2+1;
if (maxPos == i) break;
swap(a, i, maxPos);
i = maxPos;
}
}
public void swap(int[] a, int source, int target) {
int tmp = a[source];
a[source] = a[target];
a[target] = tmp;
}
}
}
# 162. 寻找峰值
二分+递归:
class Solution {
public int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {
return recursive(nums, 0, nums.length-1);
}
private int recursive(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if (r - l <= 0) {
return l;
}
int mid = (l+r)/2;
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid+1]) {
return recursive(nums, l, mid);
} else {
return recursive(nums, mid+1, r);
}
}
}
传统二分:
class Solution {
public int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int left = 0, right = n-1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + ((right-left)>>1);
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid+1]) {
right = mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < nums[mid+1]) {
left = mid+1;
}
}
return left;
}
}
# 240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
同:剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] ma, int t) {
int m = ma.length;
int n = ma[0].length;
int y = m-1;
int x = 0;
while (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < m) {
// y
while (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < m) {
if (ma[y][x] > t) {
y--;
} else if (ma[y][x] < t){
x++;
break;
} else {
return true;
}
}
// x
while (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < m) {
if (ma[y][x] < t) {
x++;
} else if (ma[y][x] > t){
y--;
break;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
更简单的做法,二叉搜索树:
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] m, int target) {
// 单向搜索,从m[y][x]开始,递归左右搜索m[y][x-1]和m[y+1][x]
if (m.length < 1) return false;
// init m[0][x-1]
int x = m[0].length-1, y = 0;
// 判断是否超出边界,如果超出边界直接返回false
while (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < m[0].length && y < m.length) {
// 判断是左还是右
if (m[y][x] == target) {
return true;
} else if (m[y][x] > target) {
x--;
} else if (m[y][x] < target) {
y++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
重刷到,写得更简洁了~
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int row = matrix.length, col = matrix[0].length;
int r = row-1, c = 0;
while (r >= 0 && c < col) {
if (matrix[r][c] == target) {
return true;
} else if (matrix[r][c] > target) {
r--;
} else if (matrix[r][c] < target) {
c++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
# 29. 两数相除
class Solution {
public int divide(int a, int b) {
if (a == 0) return 0;
if (b == 1) return a;
if (b == -1) {
if (a>Integer.MIN_VALUE) return -a;
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
long x = a;
long y = b;
int sign = 1;
if ((x>0 && y<0) || (x<0 && y>0)) {
sign = -1;
}
x = x>0?x:-x;
y = y>0?y:-y;
long res = f(x, y);
if (sign>0) {
return (int) (res > Integer.MAX_VALUE?Integer.MAX_VALUE:res);
} else {
return (int)-res;
}
}
private long f(long x, long y) {
if (y>x) return 0;
int cnt = 1;
int res = 0;
long oy = y;
while (x>=y) {
res += cnt;
x = x - y;
y = y + y;
cnt = cnt + cnt;
// System.out.println("x:"+x+"; y:"+y+"; cnt:"+cnt+"; res:"+res);
}
return res + f(x, oy);
}
}
# 166. Fraction to Recurring Decimal(分数到小数)
class Solution {
public String fractionToDecimal(int numerator, int denominator) {
if (numerator == 0) {
return "0";
}
StringBuilder fraction = new StringBuilder();
// If either one is negative (not both)
if (numerator < 0 ^ denominator < 0) {
fraction.append("-");
}
// Convert to Long or else abs(-2147483648) overflows
long dividend = Math.abs(Long.valueOf(numerator));
long divisor = Math.abs(Long.valueOf(denominator));
fraction.append(String.valueOf(dividend / divisor));
long remainder = dividend % divisor;
if (remainder == 0) {
return fraction.toString();
}
fraction.append(".");
Map<Long, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
while (remainder != 0) {
if (map.containsKey(remainder)) {
fraction.insert(map.get(remainder), "(");
fraction.append(")");
break;
}
map.put(remainder, fraction.length());
remainder *= 10;
fraction.append(String.valueOf(remainder / divisor));
remainder %= divisor;
}
return fraction.toString();
}
}
2021-10-03的每日一题,再做的时候,不用超答案了,代码逻辑也更清晰了:
class Solution {
public String fractionToDecimal(int _a, int _b) {
long a = _a, b = _b;
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
if ((a>0&&b<0) || (a<0&&b>0)) {
res.append('-');
a = Math.abs(a);
b = Math.abs(b);
}
res.append(String.valueOf(a/b));
long rem = a%b;
if (rem != 0) {
rem = Math.abs(rem);
b = Math.abs(b);
res.append('.');
Map<Long, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
StringBuilder decimal = new StringBuilder();
while (rem != 0) {
Integer index = map.put(rem, decimal.length()-1);
if (index != null) {
decimal.insert(index+1, '(');
decimal.append(')');
break;
}
rem *= 10;
decimal.append(rem/b);
rem %= b;
}
res.append(decimal);
}
return res.toString();
}
}
# 621. Task Scheduler(任务调度器)
// TODO
# 105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal(从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树)
class Solution {
// pre = [3,9,20,15,7] [root(3), left, right]
// in = [9,3,15,20,7] [left, root(3), right]
// map<root.val, index>
Map<Integer, Integer> set = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] pre, int[] in) {
for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {
set.put(in[i], i);
}
return f(pre, in, 0, pre.length-1, 0, in.length-1);
}
// p_l = pre_left p_r = pre_right
private TreeNode f(int[] pre, int[] in, int p_l, int p_r, int i_l, int i_r) {
if (p_l > p_r) return null;
int root = pre[p_l];
TreeNode r = new TreeNode(root);
int i_idx = set.get(root);
int left_len = i_idx - i_l;
r.left = f(pre, in, p_l+1, p_l+left_len, i_l, i_idx-1);
r.right = f(pre, in, p_l+left_len+1, p_r, i_idx+1, i_r);
return r;
}
}
一个月后再做:
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return recursive(preorder, 0, preorder.length-1, inorder, 0, inorder.length-1);
}
private TreeNode recursive(int[] pre, int pl, int pr, int[] in, int il, int ir) {
if (pl > pr || il > ir || pl < 0 || pr >= pre.length || il < 0 || ir >= in.length) {
return null;
}
int root = pre[pl];
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(root);
// 在中序遍历数组中找到root节点
int index = -1;
for (int i = il; i <= ir; i++) {
if (in[i] == root) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
int lsize = index - il;
node.left = recursive(pre, pl+1, pl+lsize, in, il, index-1);
node.right = recursive(pre, pl+lsize+1, pr, in, index+1, ir);
return node;
}
}
# 74. Search a 2D Matrix
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] ma, int target) {
int y = ma.length;
int x = ma[0].length;
int row = y-1;
for (int i = y-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (ma[i][0] < target) {
row = i;
break;
} else if (ma[i][0] == target) {
return true;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
if (ma[row][i] > target) {
break;
} else if (ma[row][i] == target) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
# 90. Subsets II(子集 II)
// 在#78题基础上增加set去重
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
// 为什么排序对结果有影响: [4,4,4,1,4]
Arrays.sort(nums);
dfs(nums, 0);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums, int start) {
if (start > nums.length) {
return;
} else {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
}
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (set.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
} else {
set.add(nums[i]);
}
list.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, i+1);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
}
}
← LeetCode 1 LeetCode 3 →